- Log in to post comments
Yesterday we talked about 2 of the most famous psychology experiments!
Lets continue with 2 more experiments that are equally informative and fun to learn about as the ones we read about yesterday!
The Little Albert Experiment by John Watson
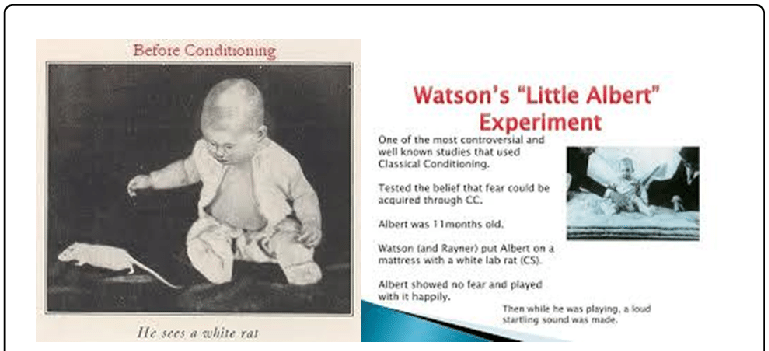
The little Albert experiment summary captures how the nine-month-old little Albert was classically conditioned to fear white rats.
A baby was brought into controlled settings called Little Albert. He was then exposed to a white rat to which he showed no fear.
But, the child began to cry when exposed to the sound of a hammer striking on a suspended steel bar. Thus, he showed no fear when exposed to the white rat in the baseline test. However, he clearly did not like the noise of the striking hammer as it frightened the child deeply.
A few months later, Watson exposed the child to the white rat again, this time with the hammer striking the metal bar. This made Little Albert cry.
Now, Watson exposed the baby to the white rat accompanied by the noise of the striking hammer continuously, a couple of times. In this way, he instilled the fear of white rats in Albert through classical conditioning. Accordingly, little Albert feared the white rat the moment he saw it.
Not only that, Little Albert feared everything that was similar to the white rat. Watson observed that Albert’s fear for the white rat transferred to other stimuli like Santa Claus mask, dog, cotton wool, etc.
Thus, the conclusion of the little Albert experiment was that humans could be conditioned for certain emotional responses , even a child !
BOBO Doll Experiment by Bandura
The aim of Bandura’s experiment was to demonstrate that if children were witnesses to an aggressive display by an adult they would imitate this aggressive behavior when given the opportunity.
Each child was shown a video of an adult hitting and yelling at an inflatable clown doll, called a 'Bobo doll.'
The children were divided into three groups: One group saw the adult punished after showing aggression towards the Bobo doll, one group saw the adult rewarded after showing aggression, and one group saw the aggression but did not see the adult either punished or rewarded for the aggression.

Next Bandura counted from a secret room how many aggressive acts - such as hitting, yelling, cursing, and punching - that each child engaged in. He found that the children who watched the adult get rewarded for showing aggression were more likely to show aggression themselves! This gave the basis for social learning theory of Bandura!
- Soumya Gulati
